
We can delete rules by find the command originally used to create them. Sudo iptables -D INPUT -p tcp -dport 22 -j ACCEPT Find Rules by Command # Or delete the rule by matching the parameters These are equivalent in our example: # Delete rule in third position in list, starting with 1 (not zero) We need to insert a rule instead of append one to allow other connections, such as https traffic: sudo iptables -I INPUT 5 -p tcp -dport 443 -j ACCEPT

Now investigate: sudo iptables -L -v HTTPS (Insert over Append) Sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -dport 80 -j ACCEPTĭrop everything else sudo iptables -A INPUT -j DROP Udp6 0 0 :46591 :* The Usual Suspects: SSH & Web TrafficĪllow future SSH connections & HTTP (port 80) traffic: sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -dport 22 -j ACCEPT Sudo iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack -ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPTĪllow/keep current related/established rules, such as our SSH connection.įind items on the top: Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State We'll setup a set of rules that will become the basic rules you can use on any server to start.Īllow data between items on the localhost network (loopback interface).

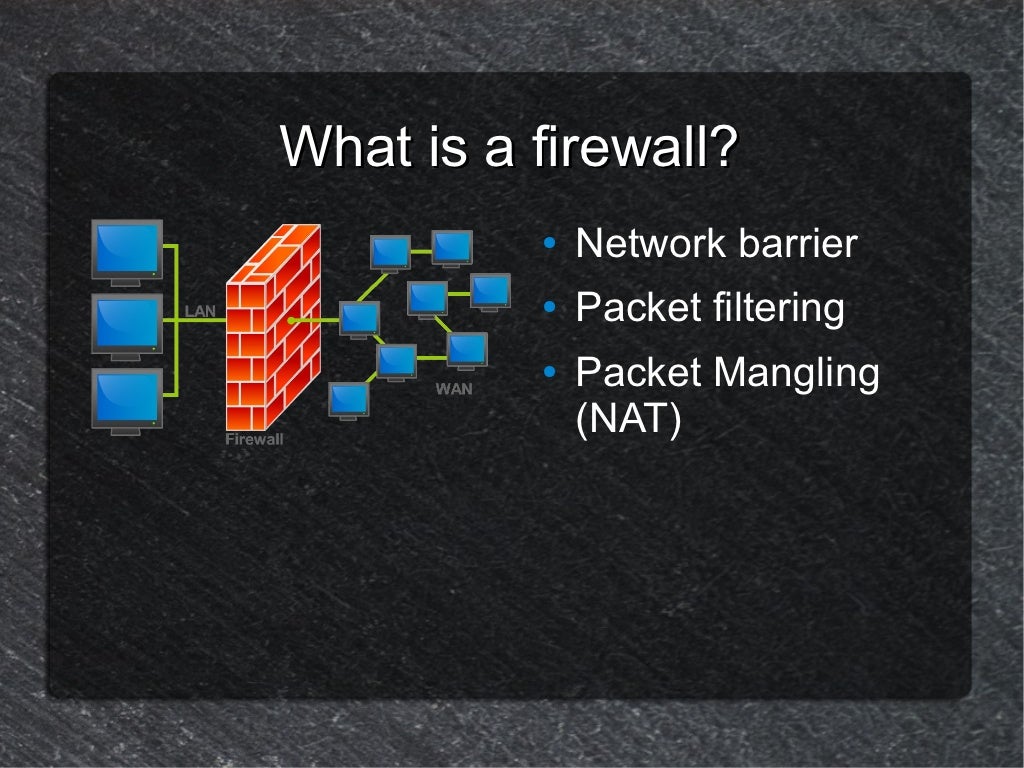
Mostly we take action on INPUT chains, which monitors incoming packets of data. Pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destinationĬhain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)Ĭhain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)ĭefault policy ACCEPT, no rules in each of the three chains. Sudo iptables -L -v Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) Here we'll discuss how to view, add and delete rules. IPtables is a default firewall you'll find in most places. Get started learning about Iptables chains, how to add/update/delete firewall rules, and start with a good basic set of rules for any server.# Firewalls


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
